Behavior
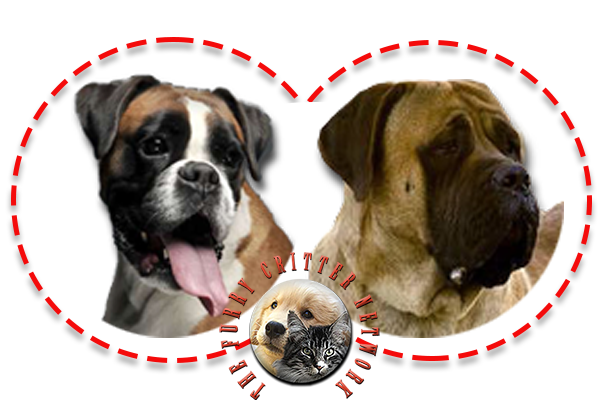
Boxers are a bright, energetic, and playful breed and tend to be very good with children. They are patient and spirited with children, but also protective, making them a popular choice for families. They are active, strong dogs that require adequate exercise to prevent boredom-associated behaviors such as chewing, digging, or licking. Boxers have earned a slight reputation of being "headstrong", which can be related to inappropriate obedience training. Owing to their intelligence and working-breed characteristics, training based on corrections often has limited usefulness. Boxers, like other animals, typically respond better to positive reinforcement techniques such as clicker training, an approach based on operant conditioning and behaviorism, which offers the dog an opportunity to think independently and to problem-solve.
The Boxer by nature is not an aggressive or vicious breed. It is an instinctive guardian and can become very attached to its family. Like all dogs, it requires proper socialization. Boxers are generally patient with smaller dogs and puppies, but difficulties with larger adult dogs, especially those of the same sex, may occur. Boxers are generally more comfortable with companionship, in either human or canine form. They are very patient and are great to adopt as family dogs because they are good with children and people of all kinds.
The Boxer can make a good house dog, but he must be given a considerable amount of exercise. His short coat requires little care.
Health
Leading health issues to which Boxers are prone include cancers, heart conditions such as aortic stenosis and arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (the so-called "Boxer cardiomyopathy"), hypothyroidism, hip dysplasia, and degenerative myelopathy and epilepsy; other conditions that may be seen are gastric dilatation volvulus (also known as bloat), intestinal problems, and allergies (although these may be more related to diet than breed). Entropion, a malformation of the eyelid requiring surgical correction, is occasionally seen, and some lines have a tendency toward spondylosis deformans, a fusing of the spine, or dystocia. Other conditions that are less common but occur more often in Boxers than other breeds are hystiocytic ulcerative colitis (sometimes called Boxer colitis), an invasive E. coli infection, and indolent corneal ulcers, often called Boxer eye ulcers.
About 22% of puppies die before reaching seven weeks of age. Stillbirth is the most frequent cause of death, followed by infection. Mortality due to infection increases significantly with increases in inbreeding.
According to a UK Kennel Club health survey, cancer accounts for 38.5% of Boxer deaths, followed by old age (21.5%), cardiac (6.9%) and gastrointestinal (6.9%) related issues. The breed is particularly predisposed to mast cell tumours, a cancer of the immune system. Median lifespan was 10.25 years. Responsible breeders use available tests to screen their breeding stock before breeding, and in some cases throughout the life of the dog, in an attempt to minimize the occurrence of these diseases in future generations.
As an athletic breed, proper exercise and conditioning is important for the continued health and longevity of the Boxer. Care must be taken not to overexercise young dogs, as this may damage growing bones, but once mature, Boxers can be excellent jogging or running companions. Because of their brachycephalic heads, they do not do well with high heat or humidity, and common sense should prevail when exercising a Boxer in these conditions.